JavaScript Tutorial: Numbers and
Mathematical Functions
[this page | pdf | back links]
JavaScript
has only one type of number (in contrast to, e.g. Visual Basic, which
differentiates between e.g. integers, floating point numbers and double
precision numbers). Numbers can be written with or without decimal points
and/or with or without (scientific) exponents, e.g.
var x = 4.1; // With a decimal point
var y = 4; // Without a decimal point
var p = 135e6 // Means 135000000
var q = 13.5e-3 // Means 0.0135
Numbers have the
following properties and methods:
Properties:
|
Property
|
Description
|
More
|
|
constructor
|
Returns object’s
constructor function
|
Here
|
|
MAX_VALUE
|
Returns largest
(positive) number recognised by the browser’s JavaScript
|
Here
|
|
MIN_VALUE
|
Returns smallest
(positive) number recognised by the browser’s JavaScript
|
Here
|
|
NEGATIVE_INFINITY
|
Represents negative
infinity (i.e. if computation overflows)
|
Here
|
|
NaN
|
Represents Not-a-Number
(i.e. if computation overflows
|
Here
|
|
POSITIVE_INFINITY
|
Represents positive
infinity (i.e. if computation overflows)
|
Here
|
|
prototype
|
Allows author to add
properties and methods to an object
|
Here
|
Methods:
|
Method
|
Description
|
More
|
|
isFinite()
|
Returns true if value is a finite number, otherwise returns false
|
Here
|
|
isInteger()
|
Returns true if value is of type
Number and is an integer (within range understood as integers by the
browser), otherwise returns false
|
Here
|
|
isNaN()
|
Returns true if value
is NaN, otherwise returns false
|
Here
|
|
isSafeInteger()
|
Returns true if value is of type Number and is a safe integer,
otherwise false. A safe integer is one that can be exactly represented as an
IEEE-754 double precision number, i.e. is an integer in the range -(253
- 1) to (253 - 1).
|
Here
|
|
toExponential()
|
Returns a string
representing the number converted into exponential form. The optional
parameter (0 to 20) represents the number of digits retained after the
decimal point
|
Here
|
|
toFixed()
|
Returns a string representing the number with a fixed number of
digits after the decimal point
|
Here
|
|
toPrecision()
|
Returns a string
representing the number with a fixed number of
significant digits
|
Here
|
|
toString()
|
Returns a string corresponding to the number
|
Here
|
|
valueOf()
|
Returns the primitive value
of an object. For a number, this in effect just returns the number itself
|
Here
|
The Math object
Associated with numbers
is the JavaScript Math object. This allows authors to carry out some
mathematical manipulations. It supports the following properties and methods:
Math object properties:
|
Property
|
Description
|
More
|
|
E
|
Returns Euler’s constant, 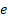
|
Here
|
|
LN2
|
Returns the natural logarithm of 2
|
Here
|
|
LN10
|
Returns the natural
logarithm of 10
|
Here
|
|
LOG2E
|
Returns the base-2 logarithm of 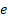
|
Here
|
|
LOG10E
|
Returns the base-10
logarithm of 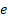
|
Here
|
|
PI
|
Returns 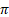
|
Here
|
|
SQRT1_2
|
Returns 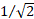
|
Here
|
|
SQRT2
|
Returns 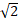
|
Here
|
Math object methods:
|
Method
|
Description
|
More
|
|
abs()
|
Returns the absolute
value of a real number
|
Here
|
|
acos()
|
Returns the (principal) arccosine of a real number
|
Here
|
|
acosh()
|
Returns the (principal)
hyperbolic arccosine of a real number
|
Here
|
|
asin()
|
Returns the (principal)
arcsine of a real number
|
Here
|
|
asinh()
|
Returns the (principal)
hyperbolic arcsine of a real number
|
Here
|
|
atan()
|
Returns the (principal)
arctangent of a real number
|
Here
|
|
atanh()
|
Returns the (principal)
hyperbolic arctangent of a real number
|
Here
|
|
atan2()
|
Returns the arctangent
of the specified x- and y-coordinates
|
Here
|
|
cbrt()
|
Returns the cube root
of a real number
|
Here
|
|
ceil()
|
Rounds
a real number towards positive infinity
|
Here
|
|
cos()
|
Returns the cosine of a real number
|
Here
|
|
cosh()
|
Returns the hyperbolic cosine
of a real number
|
Here
|
|
exp()
|
Returns the exponential of a real number (i.e. 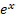 ) )
|
Here
|
|
floor()
|
Rounds a real number
towards negative infinity
|
Here
|
|
log()
|
Returns
the natural logarithm of a positive real number
|
Here
|
|
max()
|
Returns the maximum of a set of real numbers
|
Here
|
|
min()
|
Returns the minimum of
a set of real numbers
|
Here
|
|
pow()
|
Returns x to the power y. Note, ^ has a different
meaning in JavaScript
|
Here
|
|
random()
|
Returns a (uniform)
random number between 0 and 1
|
Here
|
|
round()
|
Rounds a real number to the nearest integer
|
Here
|
|
sin()
|
Returns the sine of a real number
|
Here
|
|
sinh()
|
Returns the hyperbolic
sine of a real number
|
Here
|
|
sqrt()
|
Returns the square root of a real (non-negative) number
|
Here
|
|
tan()
|
Returns the tangent of a real number
|
Here
|
|
tan()
|
Returns the hyperbolic
tangent of a real number
|
Here
|
NAVIGATION LINKS
Contents | Prev | Next | JavaScript Numbers and Math