Units commonly accepted alongside SI
units
[this page | pdf | back links]
As explained in Introduction to SI units,
there are some units that are commonly accepted alongside SI units even though
they do not specifically form part of the SI itself. These include:
Commonly used units (accepted for use with the SI), which
are defined by reference to their value in SI units:
|
Name
|
Symbol
|
Definition and value in SI Units
|
|
minute (time)
|
min
|
1 min = 60 s
|
|
hour (time)
|
h
|
1 h = 60 min = 3600 s
|
|
Day
|
d
|
1 d =24 h = 86400 s
|
|
Degree
|
°
|
1° = 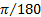 rad rad
|
|
minute (angle)
|
'
|
1' = (1/60)° = 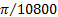 rad rad
|
|
second (angle)
|
"
|
1" =(1/3600)° = 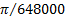 rad rad
|
|
Hectare
|
ha
|
1 ha = 1 hm2 = 104 m2, is
used to measure agrarian area
|
|
litre*
|
L, l
|
1 L = 1 dm3 = 10-3 m3
|
|
metric ton
|
T
|
1 T = 103 kg
|
|
Tonne
|
T
|
another name for metric ton
|
|
Neper**
|
Np
|
Used to measure power ratios. Uses a logarithmic scale
involving natural logarithms
|
|
Bel**
|
B
|
Used to measure power ratios. Uses a logarithmic scale
involving logarithms to base 10. Note: 1 B = 10 dB.
|
|
Decibel**
|
dB
|
Used to measure power ratios. Uses a logarithmic scale
involving logarithms to base 10. A ratio of 10 is a 10 dB change, i.e. if two
amounts (of power) differ by 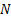 decibels
then they are in the ratio decibels
then they are in the ratio 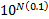 . .
|
* In the US spelt “liter” and symbol is “L”.
** These measure (power) ratios. The underlying numerical
values are rarely required, although for acoustics it is common to use 0 dB to
refer to a sound pressure of .0002 microbar or 20 micropascals (although this
is not accepted for use alongside SI units). In electronics dB may be combined
with a suffix, e.g. “m” for “milliwatt”, to make, “dBm”, so that zero dBm
equals one milliwatt, but such quantities are again not accepted for use
alongside SI units. When dB is applied to voltage, e.g. dBu or dBV, it is
necessary to square the amplitude, to convert voltage ratios to power ratios.
Another unit accepted for use with the SI is the per cent
sign (%) which in this context can be thought of as a special way of saying
0.01, i.e. 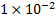 .
.
Commonly used units (accepted for use with the SI), the values
of which need to be obtained experimentally:
|
Name
|
Symbol
|
Definition and (approximate) value in SI Units
|
|
Electronvolt (or electron volt)
|
eV
|
The electron volt is the kinetic energy acquired by an
electron in passing through a potential difference of 1 V in vacuum, and is
approximately 1.602176487 x 10−19 J according to the 2006
CODATA recommended value.
|
|
astronomical unit
|
ua
|
The astronomical unit is approximately equal to the mean
Earth-Sun distance. It is the radius of an unperturbed circular Newtonian
orbit about the Sun of a particle having infinitesimal mass, moving with a
mean motion of 0.01720209895 radians per day (also known as the Gaussian
constant), and has a value of 1.49597870691 × 1011 m according to NIST
(2008).
|
|
unified atomic mass unit
|
u
|
The unified atomic mass unit is equal to 1/12 times the
mass of a free carbon 12 atom, at rest and in its ground state, and is
1.660538782 × 10−27 kg according to the 2006 CODATA
recommended value.
|
|
Dalton
|
Da
|
The dalton (Da) and the unified atomic mass (u) are
alternative names (and symbols) for the same unit
|
Terms accepted for use with the SI in certain fields /
countries due to established practice, or deemed acceptable for use with the SI
by NIST (2008):
|
Name
|
Symbol
|
Definition and value in SI Units
|
|
nautical mile
|
|
1 nautical mile = 1852 m
|
|
Knot
|
|
1 nautical mile per hour = (1852/3600) m/s
|
|
Angstrom
|
Å
|
1 Å = 0.1 nm = 10−10 m
|
|
Barn
|
b
|
1 b = 100 fm2 = 10−28 m2
|
|
Bar
|
bar
|
1 bar = 0.1 MPa = 100 kPa = 1000 hPa = 105 Pa
|
|
millimeter of mercury
|
mmHg
|
1 mmHg ≈ 133.322 Pa
|
|
curie*
|
Ci
|
1 Ci = 3.7 x 1010 Bq
|
|
roentgen*
|
R
|
1 R = 2.58 x 10−4 C/kg
|
|
rad*
|
rad**
|
1 rad = 1 cGy = 10−2 Gy
|
|
rem*
|
rem
|
1 rem = 1 cSv = 10−2 Sv
|
* Technically only accepted in the US via NIST (2008)
rather than by the SI generally.
** If there is a risk of confusion with the symbol for
radian then rd may be used instead.
NAVIGATION LINKS
Contents | Prev