HTML Element: <meter>
[this page | pdf | back links]
The HTML <meter> element indicates a
scalar measurement within a specific range (otherwise called a gauge). It can
also take fractional values. It is new in HTML 5. It is not designed to be used
to show task progress, for which the preferred element is the <progress>
element.
The attributes it can take
(other than HTML
global attributes and HTML event attributes)
include:
|
Attribute
|
Description
|
More
|
|
form
|
Name of the form that
element belongs to
|
Here
|
|
high
|
Value above which is
considered a high value
|
Here
|
|
low
|
Value below which is considered
a low value
|
Here
|
|
max
|
Maximum value
|
Here
|
|
min
|
Minimum value
|
Here
|
|
optimum
|
Value deemed optimal
for gauge
|
Here
|
|
value
|
Value of element
|
Here
|
The
high, low, max
and min attributes should
satisfy: 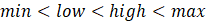 .
Not all major browsers currently support the high
and low attributes.
.
Not all major browsers currently support the high
and low attributes.
To
create or access such an element in JavaScript
see here. The
corresponding HTML DOM
object supports standard
DOM properties and methods. It also supports the following additional
properties and methods:
|
Property
|
Description
|
More
|
|
labels
|
Returns
a collection of <label>
elements corresponding to the gauge labels
|
Here
|
The default style
applicable to this element is shown here.
EXAMPLE:
HTML USED IN THIS EXAMPLE:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <!-- Copyright (c) Nematrian Limited 2018 -->
<head></head>
<body>
Created using HTML:<br>
<meter min="0" max="1" low="0.25" high="0.75" value="0.55"></meter>
<br><br>Created using JavaScript:<br>
<span id="element"></span>
<script>
var x = document.createElement("METER");
x.setAttribute("min", "0");
x.setAttribute("max", "1");
x.setAttribute("low", "0.25");
x.setAttribute("high", "0.75");
x.setAttribute("value", "0.55");
document.body.appendChild(x);
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
NAVIGATION LINKS
Contents | Prev | Next | HTML Elements