Enterprise Risk Management Formula Book
Appendix A.2: Probability Distributions:
Continuous (univariate) distributions (a) Normal, uniform, chi-squared
[this page | pdf]
Distribution name
Normal distribution
|
|
Common notation
|
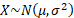
|
|
Parameters
|
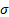 = scale
parameter ( = scale
parameter (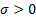 ) )
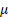 = location
parameter = location
parameter
|
|
Domain
|
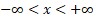
|
|
Probability density
function
|
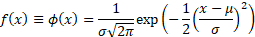
|
|
Cumulative distribution
function
|
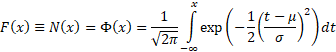
|
|
Mean
|
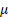
|
|
Variance
|
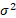
|
|
Skewness
|
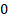
|
|
(Excess) kurtosis
|
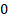
|
|
Characteristic function
|
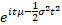
|
|
Other comments
|
The normal distribution is also called the Gaussian
distribution. The unit normal (or standard normal) distribution
is 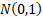 . .
The inverse unit normal distribution function (i.e. its
quantile function) is commonly written 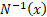 (also in
some texts (also in
some texts 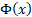 and the
unit normal density function is commonly written and the
unit normal density function is commonly written 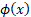 . . 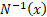 is also
called the probit function. is also
called the probit function.
The error function distribution is 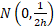 , where , where 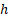 is
now an inverse scale parameter is
now an inverse scale parameter 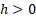 . .
The median and mode of a normal distribution are 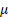 . .
The truncated first moments of 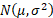 are: are:
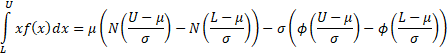
where 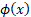 and and 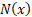 are the
pdf and cdf of the unit normal distribution respectively. are the
pdf and cdf of the unit normal distribution respectively.
The mean excess function of a standard normal distribution
is thus
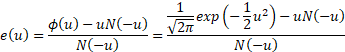
The central moments of the normal distribution are:
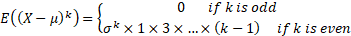
|
|
Distribution name
|
Uniform distribution
|
|
Common notation
|
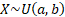
|
|
Parameters
|
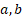 = boundary
parameters ( = boundary
parameters (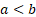 ) )
|
|
Domain
|
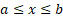
|
|
Probability density function
|
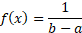
|
|
Cumulative distribution function
|
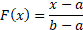
|
|
Mean
|
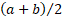
|
|
Variance
|
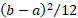
|
|
Skewness
|
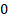
|
|
(Excess) kurtosis
|
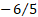
|
|
Characteristic function
|
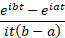
|
|
Other comments
|
Its non-central moments (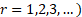 are are
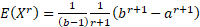 . Its
median is . Its
median is 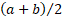 . .
|
|
Distribution name
|
Chi-squared
distribution
|
|
Common notation
|
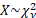
|
|
Parameters
|
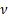 = degrees
of freedom (positive integer) = degrees
of freedom (positive integer)
|
|
Domain
|
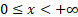
|
|
Probability density
function
|
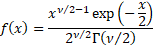
|
|
Cumulative distribution
function
|
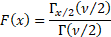
|
|
Mean
|
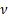
|
|
Variance
|
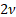
|
|
Skewness
|
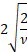
|
|
(Excess) kurtosis
|
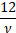
|
|
Characteristic function
|
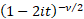
|
|
Other comments
|
Its median is approximately 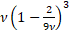 . Its mode
is . Its mode
is 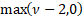 . Is also
known as the central chi-squared distribution (when there is a need to
contrast it with the noncentral chi-squared distribution). . Is also
known as the central chi-squared distribution (when there is a need to
contrast it with the noncentral chi-squared distribution).
In the special case of 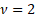 the
cumulative distribution function simplifies to the
cumulative distribution function simplifies to 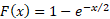 . .
The chi-squared distribution with 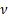 degrees
of freedom is the distribution of a sum of the squares of degrees
of freedom is the distribution of a sum of the squares of 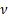 independent
standard normal random variables. A consequence is that the sum of independent
chi-squared variables is also chi-squared distributed. It is widely used in
hypothesis testing, goodness of fit analysis or in constructing confidence
intervals. It is a special case of the gamma distribution. independent
standard normal random variables. A consequence is that the sum of independent
chi-squared variables is also chi-squared distributed. It is widely used in
hypothesis testing, goodness of fit analysis or in constructing confidence
intervals. It is a special case of the gamma distribution.
As 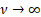 , , 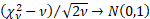 and and 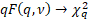
|
NAVIGATION LINKS
Contents | Prev | Next